Brian Kantor and David Holland
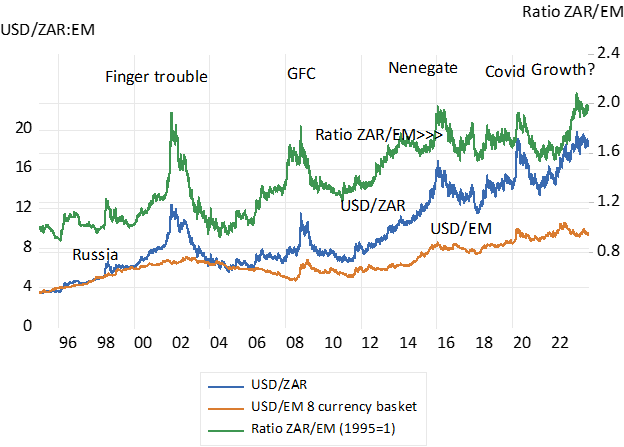
A great deal of commercial, domestic, and speculative energy is spent pondering the future of the rand (ZAR). The foreign exchange value of the rand will remain highly variable and unpredictable. The best prediction for tomorrow’s exchange rate is today’s rate but with a high level of variance that increases with time. As in the past, the rand is unlikely to be a one-way bet. It will experience periods of negative and positive turbulence. On average, persistent rand weakness is expected in the currency markets due to the higher inflation and sovereign risk of South Africa relative to the US dollar (USD) and other hard currencies. The rand cost of a US dollar is priced to rise at an average rate of 5.5% p.a. over the next five years and by about 4.5% this year. Yet, for all its volatility, changes in the foreign exchange value of the rand can be almost fully explained by but two persistent influences on its value. These are the exchange rates of other emerging market currencies with the dollar and the dollar prices of industrial metals that SA exports. 1
Since 2010, daily movements in the EM currency basket explain 54% of daily movements in the ZAR/USD exchange rate. This is a highly significant association. If you had a crystal ball that foretold future EM basket to USD rates, you could make confident and profitable bets on the trajectory of the rand’s exchange rate. Unfortunately, exchange rates are random walk processes that are impossible to precisely predict. And commodity prices also follow a random walk process. Your best guess for tomorrow’s ZAR/USD exchange rate is today’s rate plus or minus 1% (and ±2.2% if you’re looking a week ahead).
Knowing why the rand behaves as it has may however not help much to predict where it is heading. Forecasting the USD/ZAR demands an accurate forecast of the dollar value of other EM currencies and metal prices. A clearly formidable task. A strong dollar, as measured vs its developed economy peers, will clearly force EM and ZAR weakness and probably also weigh on metal prices, when expressed in USD – and vice versa. Though the major force acting on metal prices will be the state of the Chinese economy- the major destination for industrial metals – and so another known unknown with relevance for the ZAR.
The other forces acting on the rand are South African specific events. Political shocks and own goals that move the rand irregularly and unpredictably one way that then may be reversed. These shocks account for up to 46% of the movement in the rand relative to other emerging markets.
This is where wise economic policy and effective implementation of those policies can positively influence the exchange rate. The persistently weaker bias of the rand when compared to not only the US dollar, but also when compared to other emerging market currencies, is due to the failure of the South
African economy to deliver meaningful growth and attractive returns. The rand is riskier than the emerging market basket to a significant degree. A drop of 1% in the EM basket typically translates into a 1.5% drop in the rand. Government’s job is not only to shoot fewer own goals, but to convince through positive coordinated action that South Africa is not significantly riskier than other emerging markets. The potential gains are a less risky rand, a lower cost of capital, greater investment, job creation, and more wealth for the country to share.
Exchange Rates and Metal Prices (USD) Daily Data (July 2010=100)
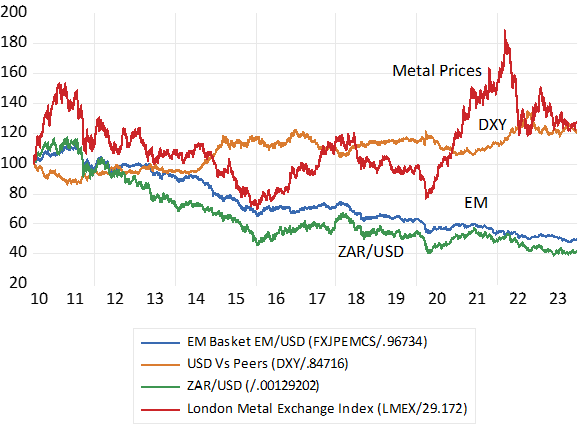
The ZAR and the EM basket. Higher number indicate rand weakness.