Does the reduced value of the S&P 500 reflect the earnings permanently lost after the coronavirus? We give a provisional answer.
The tribe of company analysts is hard at work revising the target prices (almost all lower) of the companies they follow. They will be adjusting the numerators of their present value calculations for the permanent losses of operating profits or free cash flow caused by the lockdowns. They will attempt to estimate the more long-lasting impact on the future performance of the companies they cover, after they get back to something like pre-coronavirus opportunities.
What discount rate will they apply to the expected post-coronavirus flow of benefits to shareholders? Will it be higher for the pandemic risk or lower because long bond yields are expected to remain low for the foreseeable future? When they have revised their target prices for the companies they cover, we could theoretically add up how much less all the companies covered by the analysts are now estimated to be worth. We would count the total damage to shareholders in trillions of US dollars since 1 January.
The analysts are taking much longer than usual to revise their estimates of forward earnings and target prices. But investors in shares are an impatient lot. They are making up their own collective minds, also with difficulty, as the turbulent markets and the high cost of insuring against market moves shows.
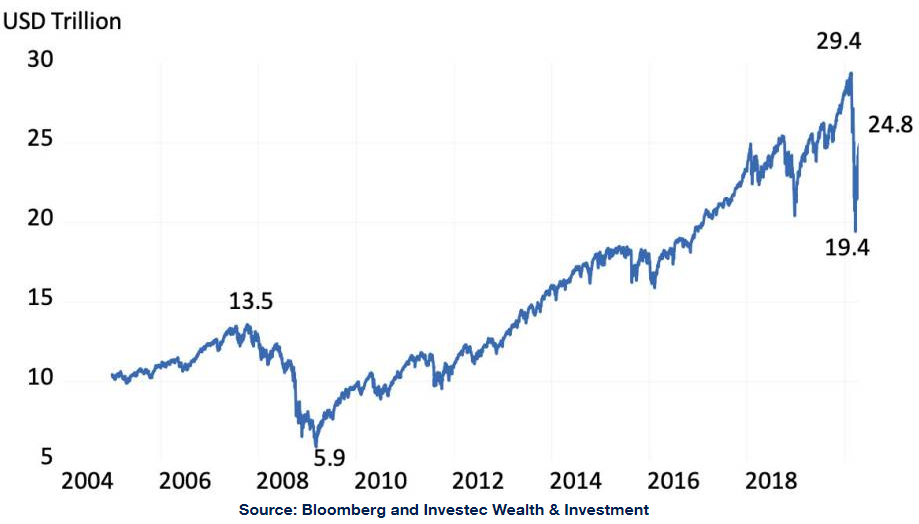
The companies listed in the S&P 500 Index were worth a collective US$28.1 trillion on 1 January 2020. By 23 February, when the market peaked, they had a still higher combined market value of US$29.4 trillion. By 23 March, the market had deducted nearly US$10 trillion off the value of these listed companies. Yet by 17 April, the market had recovered strongly from its recent lows, and was worth US$24.6 trillion, or US$3.5 trillion less than the companies were worth on 1 January. Is this too low or too high an estimate of permanent losses?
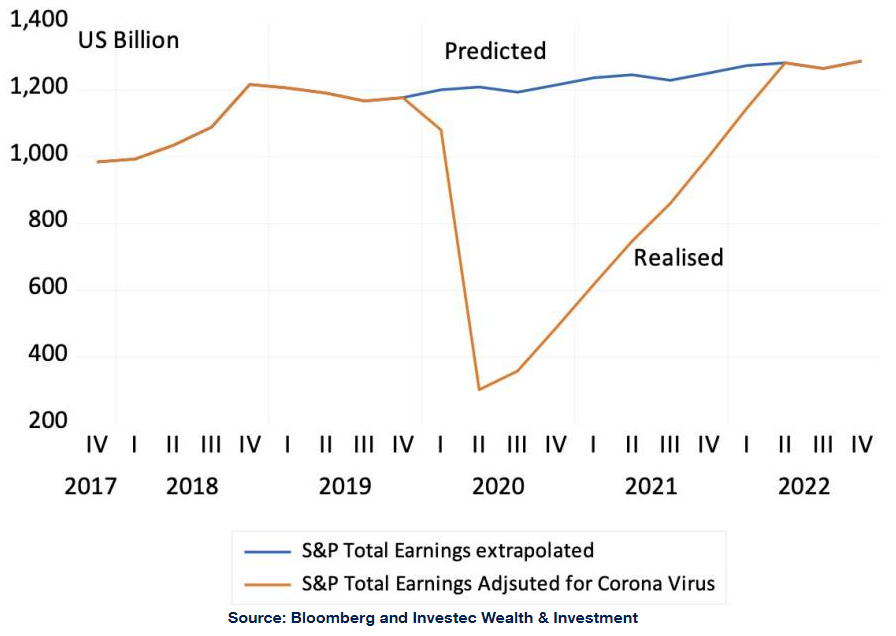
We will try to answer these questions. First, we attempt to estimate the damage to S&P reported earnings. These lost earnings can be compared with the losses registered in the market place, the US$3.5 trillion of value destruction. To do so, we first extrapolate S&P earnings beyond 2019, using a time series forecasting method. This forecast is used to establish the S&P earnings that might have been, had the economy not been so cruelly interrupted. We then estimate the earnings that are now likely to be reported, by assuming a loss ratio. That is the ratio between the earnings that we predict will be reported as a ratio to the earnings that might have been, had the US not been disrupted by the coronavirus.
As we show in the figure below, the reduction in reported earnings is assumed to be very severe in Q2 2020, when earnings to be reported in Q2 are assumed to be equivalent of only 25% of what might have been had the earnings path continued at pre-crisis levels. Then the loss ratio is assumed to decline to 30% in Q3, 50% in Q4 2020, and 75% in Q1 2021, where after it is estimated to improve by 5% a quarter until the earnings path is regained in Q2 2022.
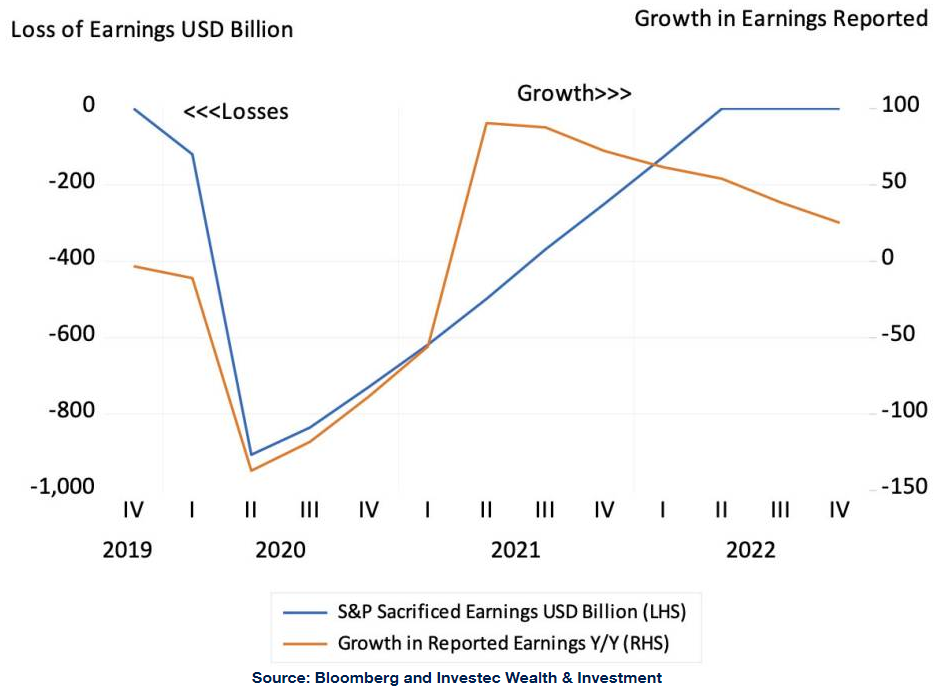
The calculations are indicated in the charts below. The total accumulated loss in earnings under these assumptions would be a large US$3.4 trillion. It will be seen that the growth in estimated S&P 500 earnings turns positive, off a very low base, as early as Q2 2021. The key assumption for this calculation is the loss ratio, as well as the time assumed to take until back to the previous path. The more elongated the shape of recovery and the greater the loss ratios, the more earnings will be sacrificed.
If this assumed permanent loss of over US$3.4 trillion were subtracted from the pre-coronavirus crisis value of the S&P 500 of US$28 trillion, it would bring the S&P roughly to the value of about US$24 trillion recorded on 17 April.